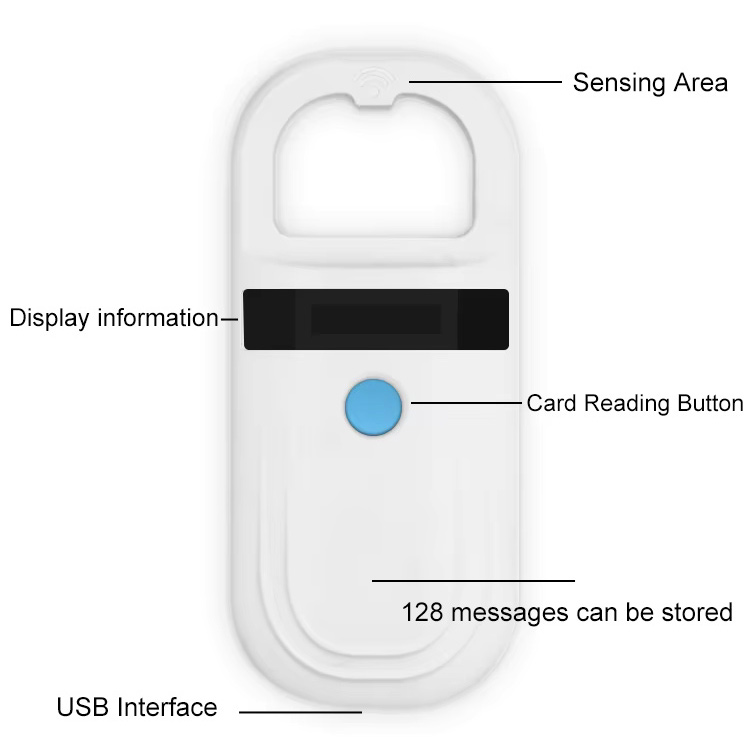
RFID Reader
A reader is the thing that reads out information from a tag or writes data to it. Depending on its design and tech, it can also be a type of writer, making it the "brain" of an RFID system. It sends radio signals around a chosen area, creating an electromagnetic field. Tags in this area respond by sending their stored data or changing it based on the reader's command. They can also talk to computer networks through interfaces. A typical reader includes: a transceiver antenna, frequency generator, phase lock loop, modulation circuit, microprocessor, memory, demodulation circuit, and a peripheral interface.
(1) Transceiver Antenna: Sends radio signals to tags and picks up their responses and info.
(2) Frequency Generator: Generates the system's operating frequency.
(3) Phase Lock Loop: Creates the needed carrier signal.
(4) Modulation Circuit: Loads the signal sent to the tag onto the carrier and sends it out via the radio circuit.
(5) Microprocessor: Makes up the signal to send to the tag, decodes the tag's response, and sends the data back to the app. If the system is encrypted, it also does the decrypting.
(6) Memory: Stores user programs and data.
(7) Demodulation Circuit: Decodes the tag's response and hands it over to the microprocessor.
(8) Peripheral Interface: Communicates with the computer.