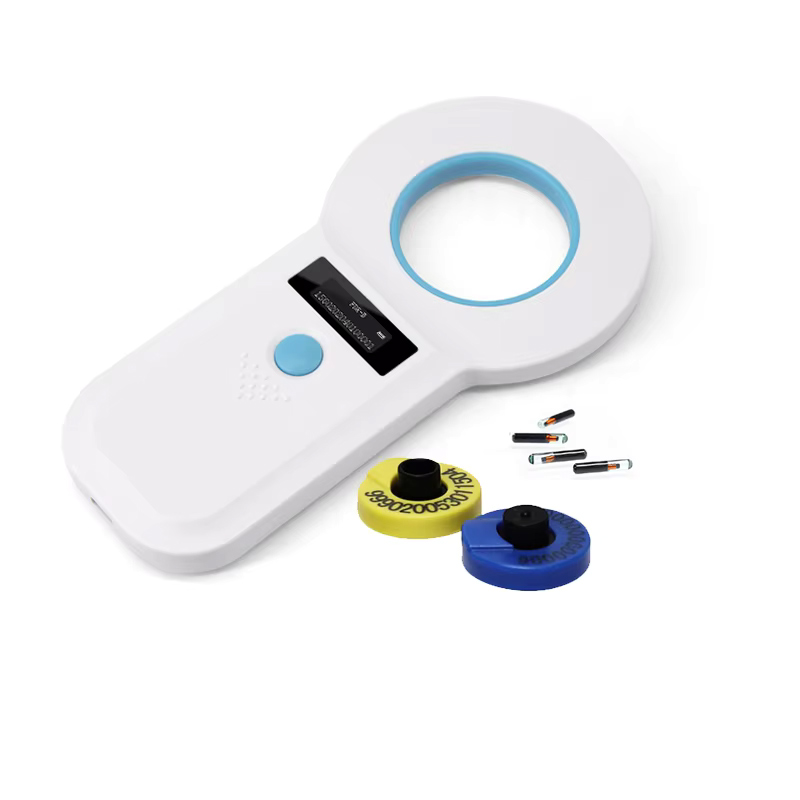
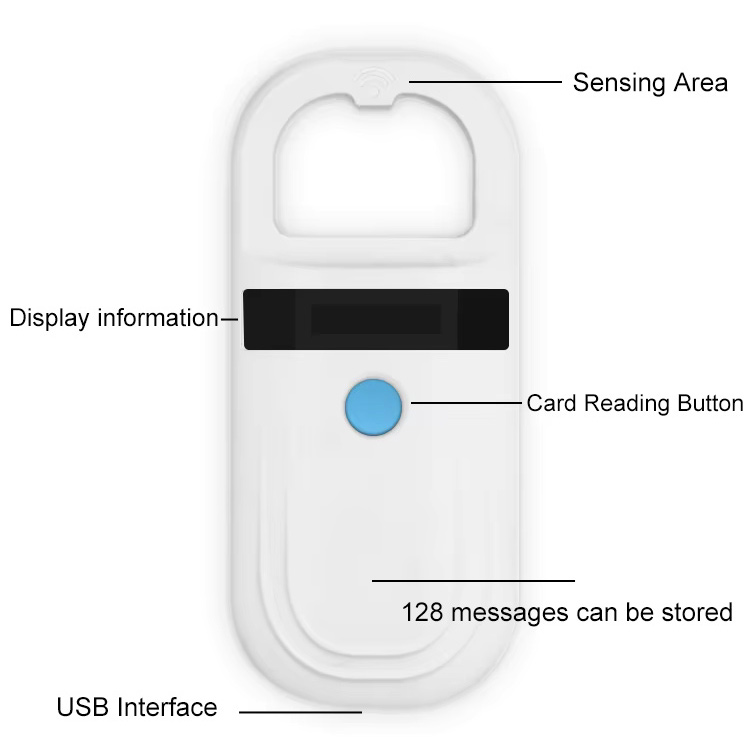
Benefits of RFID Technology
In appearance, RFID transponders are water- and magnetism-resistant for stability. In application, they offer data updating efficiently, abundant memory storage, long life span, high efficiency, and security. They streamline work by reducing labor and resources while facilitating data updates; store information in computers with a maximum capacity of several megabytes; have a long lifespan that can be reused if well maintained; enhance work efficiency through simultaneous multi-target recognition; and provide password protection against counterfeiting, making them secure. Traditional barcode technology, however, lags behind in these areas and is not suitable for current societal or industrial needs.
Disadvantages of RFID Technology
(1) Technological immaturity: The short history of RFID technology means it's not fully developed yet. Its reflectivity makes it challenging to use in metal or liquid products.
(2) High cost: RFID tags are expensive compared to regular barcodes, costing tens of times more. This can discourage the market from adopting RFID technology significantly due to its large-scale usage.
(3) Security concerns: The main security issues with RFID technology involve illegal reading and malicious tampering of tag information.
(4) Lack of standardization: