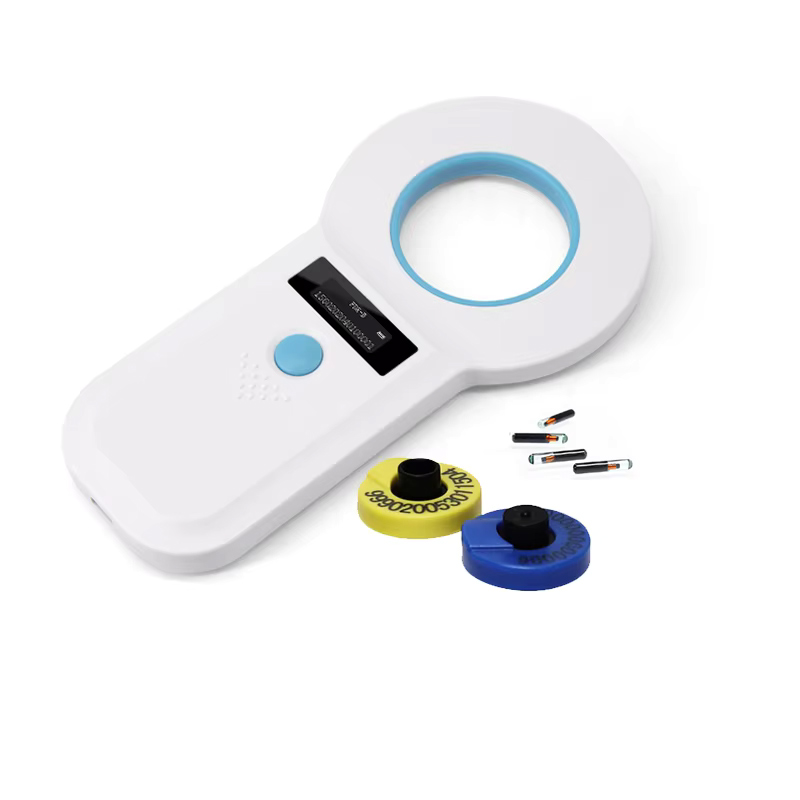
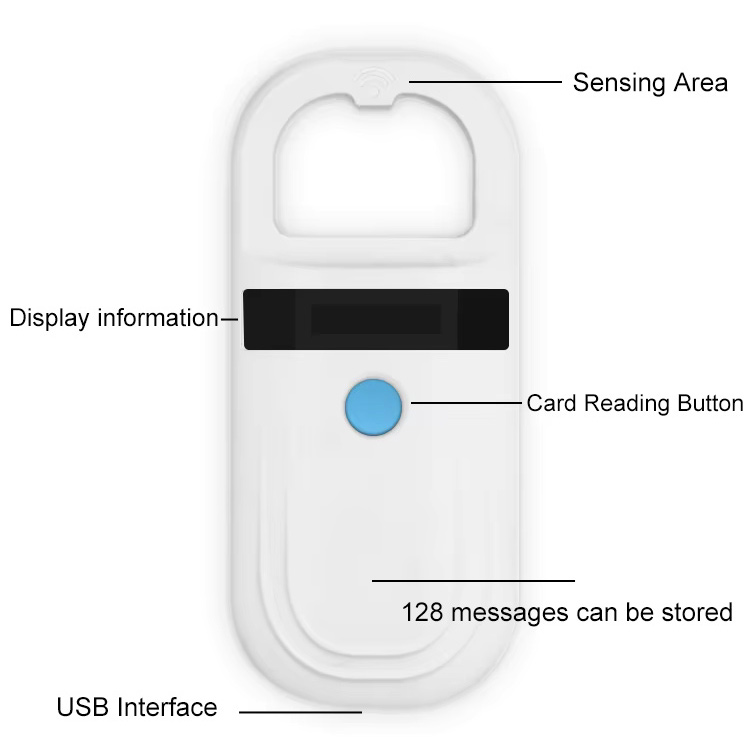
Application of Low-Frequency RFID Handheld Devices in Animal Husbandry
With the progress of science and technology, traditional animal husbandry has gradually developed into modern intelligent animal husbandry, and most animals are managed in the simplest, most convenient and fastest way. The application of RFID technology in animal husbandry has optimized the management mode and accelerated the modernization and informatization construction of animal husbandry. The application of low-frequency RFID handheld devices in animal husbandry.
Intelligent livestock breeding is an application based on key technologies of the Internet of Things. It uses RFID technology to identify animals and items, uses RFID handheld devices to identify and manage related animals and items, and transmits the data identified by RFID handheld devices to the management system to achieve the purpose of intelligent breeding and intelligent management.
I. Feeding management
When animals are born, they bind RFID tags to their livestock identities, and use RFID handheld devices to continuously set, collect or store key information such as age, gender, identity number, epidemic prevention records, disease information, etc. during the growth process. Use a low-frequency RFID mobile phone to scan the electronic tag of livestock to obtain identity information and count livestock according to different codes. Before being put on the market, the RFID handheld device reads the RFID electronic ear tag, and the livestock can be put on the market only after confirming that they are healthy and free from diseases.
II. Slaughter identification
Before slaughtering, use an RFID handheld device to read the RFID electronic ear tag on the livestock to confirm that the livestock has been registered for epidemic prevention and is healthy before entering the slaughterhouse for slaughter and flowing into the market.
III. Logistics and distribution link
After slaughtering is completed, fresh meat enters the circulation link, and RFID tags are affixed to trays or packaging boxes containing meat. Before transportation, use an RFID handheld device to scan the RFID tag to generate a list; after arriving at the destination, use the RFID handheld device to scan the tag again for confirmation, and check and verify the two lists to avoid omissions and other situations.