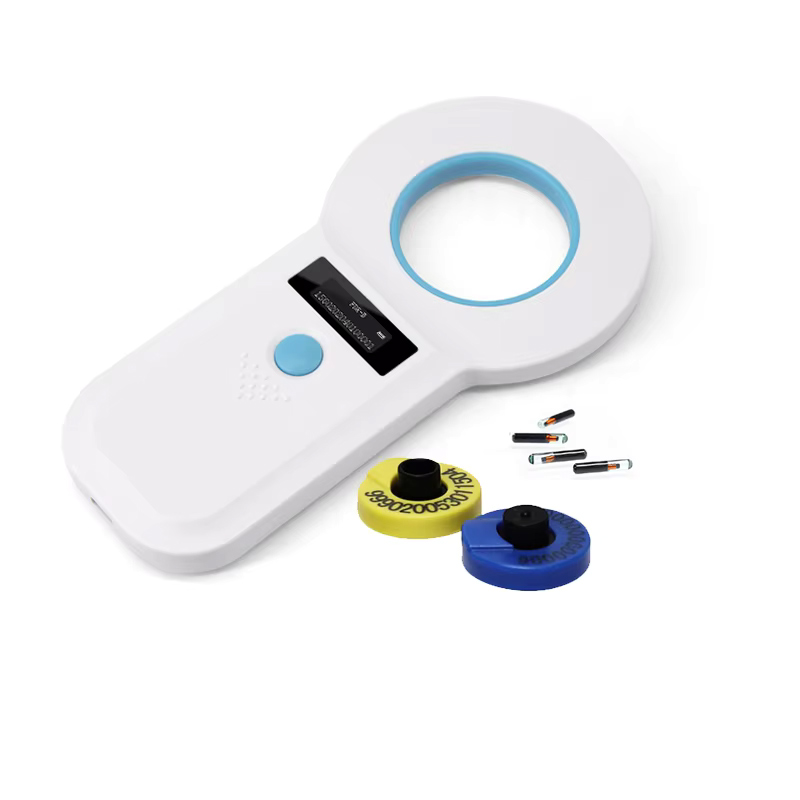
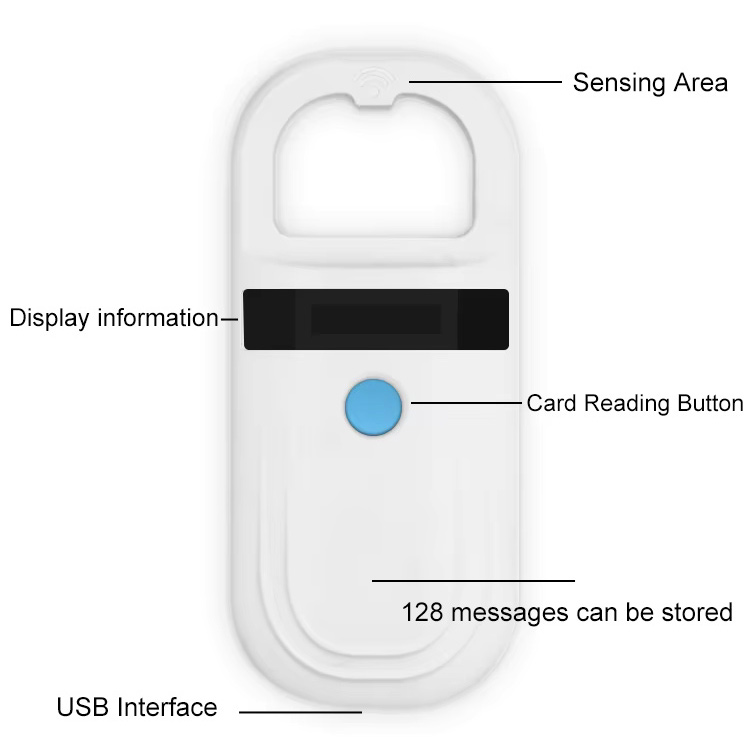
An animal chip reader, also known as an animal microchip scanner or pet scanner, is a device designed to read and identify the unique identification codes stored within radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips implanted in animals. These microchips are commonly used for pet and livestock identification and tracking purposes.
The technology behind the animal chip reader operates based on ISO standards, typically conforming to ISO 11784/85, ensuring compatibility with various types of animal identification chips worldwide. The reader works by emitting a low-energy radio signal that activates the passive RFID chip when it comes within range. The chip, which is usually encased in biocompatible glass and is very small (often comparable in size to a grain of rice), absorbs this energy and uses it to transmit its unique ID code back to the reader.
The reader then decodes this information and displays it, either on a simple LED screen showing the code or, in more advanced models, connecting to a computer or mobile device via Bluetooth or USB, providing additional details about the animal such as owner information, medical history, or registration details that are stored in a related database.
Animal chip readers are handheld, portable devices that are user-friendly and battery-powered, making them convenient for use in veterinary clinics, animal shelters, customs checkpoints, and by individual pet owners. They play a crucial role in reuniting lost pets with their owners, facilitating animal control and welfare services, and managing livestock in agricultural settings. The robust design of these readers, including features like waterproofing and drop resistance, ensures they can withstand the demands of various environments where animals are present.